Analyzer Algorithm¶
Comprehensive mathematical definitions can be found here LaTeX.
The Analyzer subdivides into half-circles, represented by only one tangent on-curve control point per half-circle.
This is the equivalent of four hyperbolic / two parabolic subsegments.
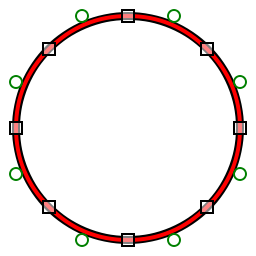
The following quadratic bezier spline encoding has the advantage of reducing data and finding meaningful points for further computational comparison while preserving most of the visual representation.
There are six types of feature TURNS. Two symmetric types stacked on top of each other, facing opposite directions become a non-symetric type:
2 Swing = 1 Crest
2 Dune = 1 Spike
2 Cliff = 1 Spiral
CORNERS are maxima surrounded/terminated by Turns (TCT). Turns also include Start/End points. This is the final representation format after analysis. It is used for overlay comparison in the Comparator:
The difference between a sinusoid Swing’s Corner and a Crest’s Turn:
The frontside Crest in the first result is preferred over the backside Swing in the second result. Detection has to be performed in both directions:
There has to be an even number of Cliffs which are centered from both sides. These Results are invalid:
An explanation with a slightly outdated terminology. Straights refer to Dunes:

